I had a tough time differentiating between stinging nettle vs catnip before. Now that I’ve already figured it out I wanted you to get a clear idea on how to identify them. All the differences and similarities are clearly described here for your convenience. So keep on reading.
What Is Stinging Nettle?
Stinging Nettle (Urtica dioica) is a perennial herbaceous plant known for its unique defensive mechanism and diverse applications. Its serrated, heart-shaped leaves and stems are covered with tiny, hair-like structures that release a potent mix of chemicals upon contact, causing a stinging sensation, itching, and mild irritation to the skin.
Despite its defensive reputation, Stinging Nettle has been utilized for centuries in traditional medicine and culinary practices. Rich in nutrients, it has been used as a potential remedy for allergies, arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.
When properly processed, the plant’s leaves can also be cooked and consumed as a nutritious food source. Beyond its medicinal and dietary uses, Stinging Nettle growing holds cultural significance in various societies and continues to intrigue researchers exploring its multifaceted benefits and properties.
What Is Catnip?
Catnip (Nepeta cataria) is a perennial herbaceous plant belonging to the mint family. Renowned for its intriguing effect on cats, Catnip possesses aromatic leaves that contain a compound called nepetalactone.
When cats come into contact with or inhale the scent of catnip, they often exhibit playful, hyperactive, or euphoric behaviors, including rolling, rubbing, and purring. This reaction, which lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes, is thought to be a response to the nepetalactone compound stimulating sensory receptors in a cat’s brain.
Cat owners often use dried or fresh catnip leaves as a recreational enrichment tool for their feline companions, incorporating it into toys, scratching posts, or simply allowing their cats to interact with the plant directly. While catnip has a fascinating impact on cats, it is relatively harmless and safe, making it a popular addition to indoor feline environments.
Visual and Sensory Identification Guide: Stinging nettle vs Catnip
Being able to tell the difference between stinging nettle and catnip at a glance can save gardeners time, and sometimes, a painful surprise. Use this quick guide to spot each plant through leaf shape, stem feel, and scent clues.
Leaf Shape and Texture
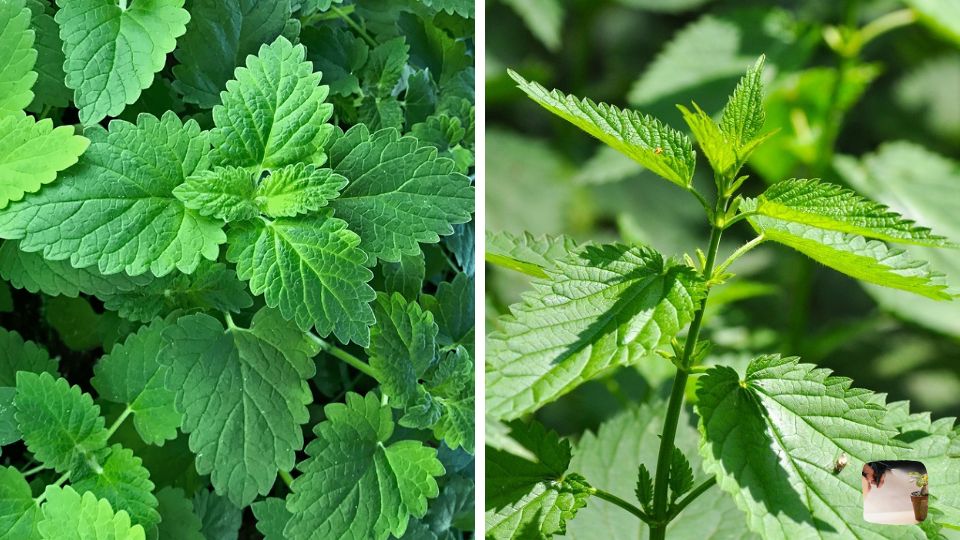
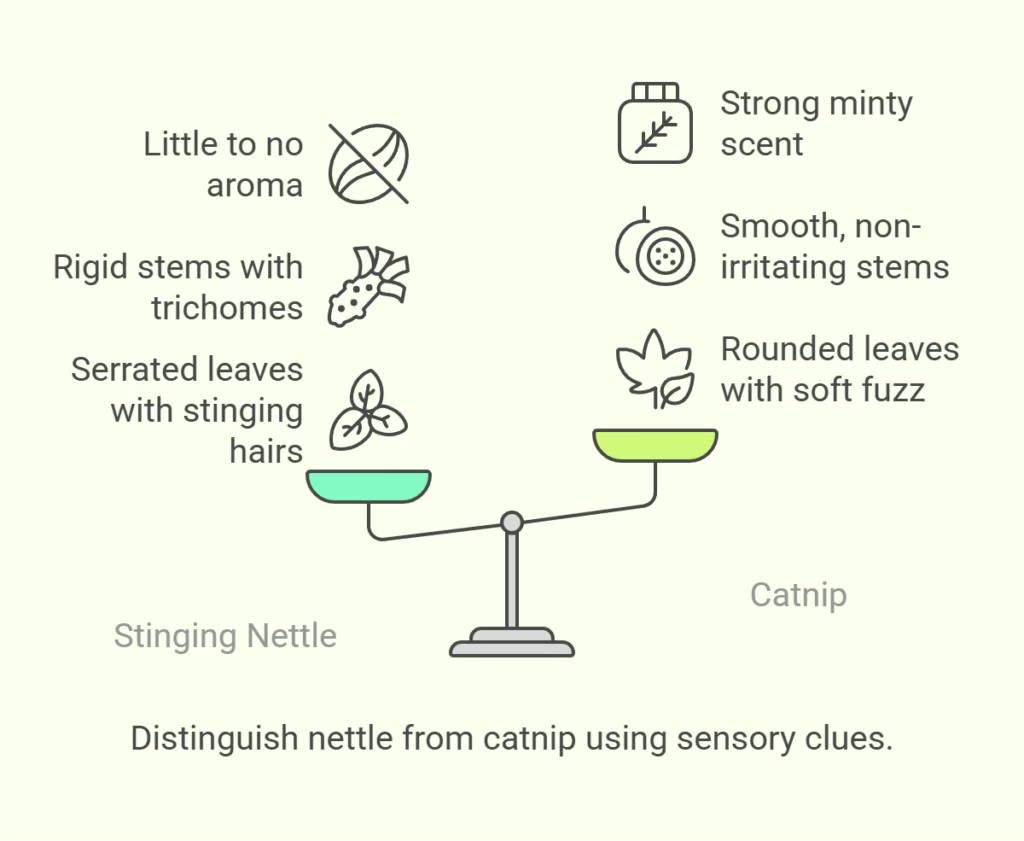
Stinging nettle leaves are deep green, serrated, and shaped like a heart. They’re covered in fine stinging hairs, which trigger skin irritation on contact. The surface feels coarse and slightly bristly to the touch.
In contrast, catnip leaves are light green, fuzzy, and shaped more like rounded triangles. The texture is soft and velvety, making it a favorite for cats and safe to handle barehanded.
Stem Characteristics
Both plants feature square stems, a trait common in many herbs. But their textures differ significantly.
Stinging nettle stems are rigid and lined with tiny stinging trichomes, making them rough and painful to brush against. These hairs can release compounds like histamine and formic acid, causing a temporary burning or itching feeling.
Catnip stems, on the other hand, are also square but much smoother and non-irritating. They’re often slightly hairy but don’t contain any stinging elements, making them easy to trim or harvest.
Aroma and Scent
The scent test is a fast way to identify catnip versus nettle. Stinging nettle has little to no aroma, even when leaves are crushed.
Catnip, however, releases a strong, minty scent when touched. This aroma comes from nepetalactone, the same compound that triggers playful behavior in cats.
Similarities Between Stinging Nettle and Catnip
Stinging Nettle (Urtica dioica) and Catnip (Nepeta cataria) are two distinct plants with unique characteristics, yet they share certain similarities that contribute to their botanical intrigue and historical significance. In, Stinging Nettle vs Catnip their differences in usage and effects, these similarities offer insights into the diverse ways plants interact with humans and the animal kingdom.
Heart-Shaped Leaves
Both Stinging Nettle and Catnip exhibit heart-shaped leaves, albeit with variations in size, color, and texture. This resemblance in leaf shape is an interesting commonality between the two plants.
Perennial Growth
Both plants are perennials, meaning they have a lifecycle that extends beyond two years. This perennial nature allows them to persistently thrive and contribute to their ecosystems year after year.
Medicinal Traditions
Stinging Nettle and Catnip have historical ties to traditional medicine in various cultures. While their applications and effects differ significantly, both have been employed for their potential health benefits. Stinging Nettle has been used for its anti-inflammatory properties, while Catnip has been utilized to induce relaxation in herbal remedies.
Cultural Significance
Both plants hold cultural significance in different societies. Stinging Nettle, despite its stinging nature, has been embraced as a valuable source of food, fiber, and medicine when properly prepared. Catnip, on the other hand, is celebrated for its entertaining effect on cats, reflecting a lighter and more playful cultural connection.
Interaction with Living Organisms
Both Stinging Nettle and Catnip interact with living organisms in distinctive ways. Stinging Nettle’s stinging hairs deter herbivores and serve as a natural defense mechanism, while Catnip’s aroma elicits playful behaviors in cats, showcasing the fascinating interplay between plants and animals.
Chemical Complexity
Both plants contain a variety of chemical compounds that contribute to their effects. Stinging Nettle’s stinging sensation is caused by chemicals released from its hairs, while Catnip’s intriguing impact on cats is attributed to the compound nepetalactone.
Botanical Diversity
Despite their shared similarities, Stinging Nettle and Catnip belong to different botanical families. Stinging Nettle is part of the Urticaceae family, while Catnip is a member of the Lamiaceae (mint) family. This showcases the incredible diversity of plant life and adaptation strategies.
The shared characteristics of heart-shaped leaves, perennial growth, medicinal traditions, cultural significance, interactions with living organisms, chemical complexity, and botanical diversity provide a fascinating glimpse into the complex world of plants and their interactions with both humans and animals.
Stinging Nettle vs Catnip: At a Glance
Here’s a concise table highlighting the similarities and differences between Stinging Nettle and Catnip:
| Characteristic | Stinging Nettle | Catnip |
| Physical Appearance | Serrated heart-shaped leaves | Gray-green heart-shaped leaves |
| Stinging Effect | Causes stinging sensation | Elicits playful cat behaviors |
| Medicinal Uses | Potential anti-inflammatory | Used in herbal remedies |
| properties, food, and fiber | for calming cats | |
| Cultural Significance | Traditional medicinal plant | Used for cat enrichment |
| Chemical Compounds | Stinging hairs contain irritants | Nepetalactone induces response |
| Plant Family | Urticaceae | Lamiaceae (mint family) |
| Interactions | Defensive mechanism against | Elicits cat’s sensory response |
| herbivores | and playful behaviors |
Would you like to know which one is the best compost for your garden between black kow vs miracle grow? You can take a quick peek.
Differences Between Stinging Nettle and Catnip
Stinging Nettle (Urtica dioica) and Catnip (Nepeta cataria) may possess certain superficial similarities, but their differences are more pronounced and extend across various aspects. So, check some aspects on Stinging Nettle vs Catnip:
Effect on Organisms
- Stinging Nettle: Upon physical contact, the fine hairs on Stinging Nettle’s leaves and stems release chemicals that cause a stinging sensation and skin irritation in humans.
- Catnip: Catnip elicits a unique response in cats, characterized by playfulness, hyperactivity, rolling, rubbing, and purring when they smell or interact with the plant.
Physiological Response
- Stinging Nettle: Its stinging hairs provoke a histamine response, leading to localized discomfort on the skin.
- Catnip: Cats react to the compound nepetalactone, which interacts with sensory receptors in their brains, triggering behavioral changes.
Intended Audience
- Stinging Nettle: Primarily interacts with and affects humans, causing irritation when touched.
- Catnip: Mainly appeals to cats, providing them with a form of recreational entertainment.
Use in Medicine
- Stinging Nettles: Historically used for its potential medicinal benefits in humans, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Sting nettle seeds are also very useful.
- Catnip: Used in herbal remedies for humans, often as a mild sedative, but its more pronounced impact is on cats.
Cultural Significance
- Stinging Nettles: Used for food and fiber in some cultures, it also carries folklore and historical importance.
- Catnip: Holds a unique place in pop culture due to its effect on cats, leading to its integration into toys and enrichment items for feline companions.
Plant Characteristics
- Stinging Nettle: Leaves and stems are covered in stinging hairs that release irritants.
- Catnip: Leaves have a gray-green color and a distinctive minty aroma that cats find attractive.
Wildlife Interaction
- Stinging Nettle: Serves as a host plant for butterfly species, contributing to local ecosystems.
- Catnip: Primarily affects domesticated cats, enhancing their environment through playful behaviors.
Chemical Composition
- Stinging Nettle: Contains various compounds, including histamines and flavonoids, contributing to its stinging effect.
- Catnip: Contains nepetalactone, the compound responsible for its characteristic cat-attracting scent.
Impact on Gardens
- Stinging Nettle: Can be considered a weed due to its invasive nature in gardens and agricultural areas.
- Catnip: Sometimes intentionally cultivated to attract and entertain cats.
While both Stinging Nettle and Catnip have intriguing aspects and historical uses, their primary effects, intended audiences, and ecological roles are distinct. Stinging Nettle engages with humans in multifaceted ways, from medicine to folklore, while Catnip captivates cats and enhances their well-being through playful interactions.
Ecological Roles and Garden Benefits
Understanding the garden value and ecological roles of both stinging nettle and catnip can help you make smart planting choices. These plants don’t just look good, they offer real benefits for pollinators, soil health, and even household pets.
Stinging Nettle in the Ecosystem
Stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) plays a surprisingly helpful role in the garden. While its sting might discourage touch, it’s a pollinator-friendly plant that supports butterflies like the Red Admiral. It also improves soil structure by pulling nutrients from deep layers with its roots, which naturally enriches nearby plants.
Gardeners often use stinging nettle to make organic liquid fertilizer or compost starter. Its leaves break down quickly and add trace minerals that improve soil fertility. For those building a sustainable garden ecosystem, nettle offers both biodiversity and soil-enhancing power.
Catnip’s Role in Gardens
Catnip (Nepeta cataria) is more than a cat favorite, it’s a low-maintenance herb that boosts garden health. Thanks to its strong scent, rich in nepetalactone, it acts as a natural insect repellent, helping keep pests like aphids and squash bugs away.
Catnip also attracts beneficial pollinators like bees and butterflies, helping your flowering and fruiting plants thrive. Plus, when grown in containers or garden beds, it provides safe, stimulating sensory enrichment for indoor or outdoor cats.
Whether you’re creating a pollinator garden, improving soil vitality, or looking for pet-friendly landscaping ideas, both plants can serve unique, eco-conscious roles in your growing space.
FAQs
Can Stinging Nettle be used for anything other than causing stinging sensations?
Yes, despite its stinging hairs, Stinging Nettle has been used in traditional medicine for its potential anti-inflammatory properties and as a source of food and fiber when properly processed.
Is Catnip safe for all cats?
Yes, most cats exhibit playful behaviors in response to Catnip. However, not all cats are affected, as sensitivity to nepetalactone is genetic. Kittens and elderly cats are less likely to respond, while some cats may not show any interest at all.
Are there any precautions to take when handling Stinging Nettle or Catnip?
When handling Stinging Nettles, wearing protective gloves is advised to avoid the stinging hairs. For Catnip, there are no significant precautions for humans, but it’s important to moderate a cat’s exposure to prevent overstimulation or habituation to its effects.
Lastly, I wanted to suggest another article that I covered earlier, beginner-friendly tips and tricks for balcony gardening.
borshon96
Recommended

9 Effective Tips for Balcony Gardens for Beginners

Best Homemade Fertilizer: Banana Peel for Plants


Philodendron Neon Heartleaf: Your Most Obedient Houseplant