Growing Maple Trees in Hot Weather: Tips & Facts
Last year my friend moved to a tropical climate area. She wanted to have healthy growth for her maple trees there as before. But she was confused and asked me, Is growing maple trees in tropical climate possible?
I searched about it and found out that growing maple trees in tropical climate is feasible, if certain measures are taken. And you must be here to learn about the same fact, right?
Keep reading to know tips and tricks on maple tree growth in a tropical climate.
Suitable Climate for Growing Maple Trees
Maple trees, renowned for their stunning foliage and delicious syrup, flourish in specific climates conducive to their growth. The ideal habitat for maple trees encompasses temperate regions, where they thrive in conditions that balance warmth and cold.
Temperate Zones: The Ideal Habitat
Maple trees thrive in temperate zones characterized by moderate temperatures and distinct seasons. These habitats provide the ideal conditions for maple tree growth, with well-drained soil and adequate sunlight.
Temperate climates offer the necessary balance of warmth and cold, fostering healthy foliage, vibrant colors, and prolific sap production in maple trees.
Chilling Requirements for Dormancy
One of the defining features of temperate climates is the presence of cold winters. For american red maples, these chilly months play a pivotal role in their growth cycle. The chilling period, where temperatures drop significantly, prompts maples to enter a state of dormancy.
During this phase, metabolic activity decreases, and the trees conserve energy until warmer temperatures return. This dormancy is essential for the overall health and longevity of the tree, as it allows them to reset and prepare for new growth in the following spring.
Summer Sun and Fall Transformation
Maples are also reliant on the warm summers typical of temperate zones. The ample sunlight during this season fuels photosynthesis, the process by which trees convert sunlight into energy.
This energy is vital for the tree’s growth and development, as well as the production of sugars that are stored and utilized during the dormant period. As summer transitions into fall, the changing balance of daylight and temperature triggers the iconic color change of maple leaves.
The vivid hues of red, orange, and yellow are spectacular results of complex chemical reactions within the leaves.
Rainfall and Soil: Supporting Growth
In addition to temperature variations, temperate climates often provide consistent and well-distributed rainfall throughout the year. This steady supply of moisture is crucial for small maple trees, as it ensures that they have access to adequate water for growth and development.
Furthermore, the soils in temperate regions tend to be diverse and rich in nutrients, offering maples the necessary elements to thrive.
Can You Grow Maple Trees in Tropical Climate?
Maples, renowned for their stunning autumn foliage and iconic shape, has long been associated with temperate climates, particularly in regions with distinct seasons.
However, the desire to cultivate these captivating trees in tropical climates has led to explorations into their adaptability and the challenges that arise when attempting to grow them in such environments.
The Adaptability of Maple Trees
Maples belong to the genus Acer and encompass a diverse range of species, each with its unique characteristics and preferences. While most traditional maple species are native to temperate zones, there are varieties that show varying levels of adaptability to tropical and subtropical climates.
Some factors that influence adaptability include species-specific characteristics, local microclimates, and the level of human intervention to create suitable conditions.
Challenges in Growing Maple Trees in Tropical Climates
Growing maple trees in tropical climates present a series of challenges primarily rooted in the fundamental differences between these climates and the temperate zones where maples naturally thrive.
- Lack of Dormancy: One of the most significant challenges is the absence of cold winters that induce dormancy in maples. Dormancy is a critical period for the trees to rest, rejuvenate, and prepare for new growth. Without this dormancy, maples in tropical regions may struggle to maintain their health and vitality.
- Temperature Extremes: Tropical climates are characterized by consistently high temperatures and humidity levels, which can be detrimental to small maple trees that are adapted to temperate conditions. Prolonged exposure to extreme heat can stress the trees, affect their growth patterns, and lead to leaf scorch.
- Daylight Patterns: Maples in temperate zones are attuned to the changing daylight patterns associated with distinct seasons. In tropical regions, day length remains relatively consistent throughout the year, disrupting the natural cues that maples rely on for growth, flowering, and foliage changes.
- Pests and Diseases: The warmer, more humid conditions in tropical climates can create a favorable environment for various pests and diseases that maples are not well-equipped to handle. This can lead to increased vulnerability and potential damage to the trees.
Despite the challenges, there are potential strategies to explore when growing Maple Trees in tropical climates.
Benefits of Growing Maple Trees in Tropical Regions
Maple trees may be best known for thriving in temperate zones, but with the right care, they can also bring unique advantages to tropical gardens.
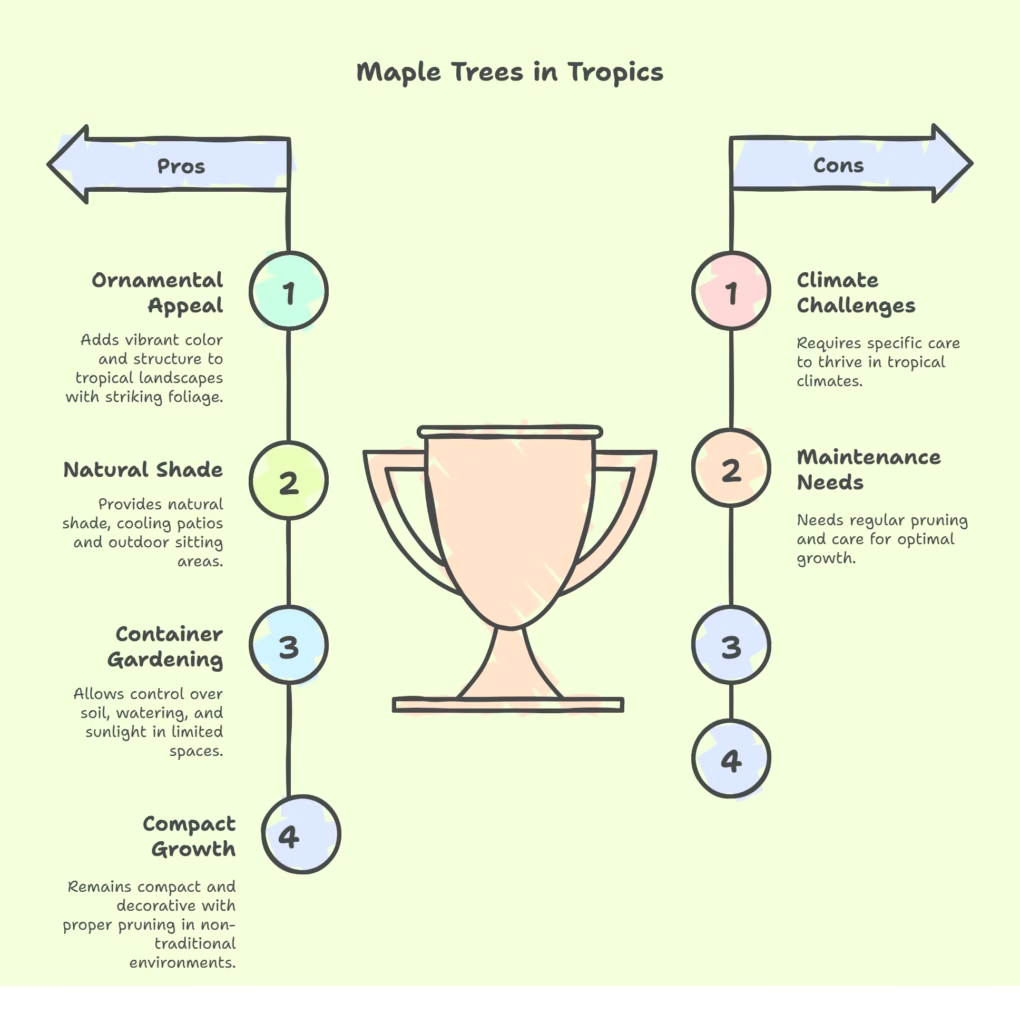
Ornamental Appeal and Shade
Maple trees offer striking foliage that adds vibrant color and structure to any landscape. Even in warm climates, species like the Japanese maple can deliver beautiful leaf patterns and seasonal variations. Their wide canopy provides natural shade, making them ideal for cooling patios, pathways, or outdoor sitting areas.
Container Gardening for Small Spaces
In tropical climates where garden space may be limited, growing maple trees in containers is a smart solution. It allows better control over soil conditions, watering, and sunlight exposure.
Potted maples can be moved to shaded spots during extreme heat and offer flexibility in urban or balcony gardens. With proper pruning and care, they remain compact, decorative, and easy to maintain even in non-traditional environments.
Tips for Growing Maple Trees in Tropical Climate
Cultivating maple trees in a tropical climate presents a unique set of challenges due to the stark contrast between the tree’s natural habitat and the conditions found in tropical regions.
So, can maple grow in tropical climate? However, with careful planning, adaptation, and the right techniques, it is possible to create an environment where maple trees can thrive and exhibit their iconic beauty even in non-temperate zones.
Here are some elaborative tips to consider when attempting to grow maple trees in a tropical climate:
Choose the Right Maple Species
Begin by selecting maple species that have shown some level of adaptability to warmer climates. Varieties like the Japanese maple (Acer palmatum) and the red maple (Acer rubrum) are among those that might tolerate tropical conditions better than others.
Microclimate Creation
Creating a suitable microclimate within your garden is essential. Start by choosing a location that receives filtered sunlight or partial shade. Placing the small maple tree under the canopy of larger trees or using shade cloths can help protect it from the intense tropical sun.
Soil Preparation
Prepare well-draining soil rich in organic matter. Amending the soil with compost can help improve its water-holding capacity and nutrient content. Adequate soil drainage is crucial to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot.
Watering Practices
Watering practices must strike a balance between providing consistent moisture and avoiding waterlogged conditions. Monitor the soil moisture regularly and water when the top inch of soil feels dry. Adjust the frequency based on humidity levels and rainfall.
Fertilization
Maple trees require essential nutrients for growth and health. Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer to provide the tree with the necessary nutrients. Avoid over-fertilization, which can lead to excessive growth and weaker branches.
Pruning and Training
Regular pruning is crucial to manage the growth of the maple leaf tree and encourage healthy branching. Pruning can also help create a more open canopy, allowing better air circulation and reducing the risk of disease.
Mulching
Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree to help retain moisture, regulate soil temperature, and suppress weed growth. However, ensure that the mulch does not come into direct contact with the tree trunk.
Temperature and Humidity Control
Consider employing cooling strategies to regulate temperature and humidity. Misting the tree during the hottest parts of the day or using shade cloth can help create a more favorable environment.
Artificial Dormancy
Although inducing a true dormancy period in a tropical climate can be challenging, you can still create a period of reduced activity by adjusting watering and fertilization during the cooler months. This can mimic the rest period that maples experience during winter.
Container Cultivation
Growing American red maples in containers can offer more control over the growing environment. Use a large container with excellent drainage and quality potting mix. This approach allows you to move the tree to a more suitable location if conditions become unfavorable.
Pest and Disease Management
Monitor the maple tree regularly for signs of pests and diseases common in tropical climates. Act promptly to address any issues and consider using natural or organic remedies to minimize chemical interventions.
Patience and Adaptation
Growing maple trees in a tropical climate require patience and a willingness to adapt your strategies based on the tree’s response and changing conditions. Not all attempts may be successful, but learning from each experience will contribute to your understanding of maple cultivation in the tropics.
Through careful selection of species, attention to microclimate, and thoughtful care practices, you can create a suitable environment that allows maple trees to thrive and showcase their beauty even in the midst of a tropical landscape.
Growing Maple Trees in Container
Cultivating maple trees in containers offers a practical solution for enthusiasts in various climates, including tropical regions. Choose a suitable maple leaf tree variety with adaptability to container growth, such as the heat tolerant Japanese maple (Acer palmatum).
Begin with a large container that provides ample room for root growth, ensuring it has proper drainage. Employ a well-draining, nutrient-rich potting mix.
Place the container in a location that balances sunlight exposure; filtered sunlight or partial shade is ideal to protect the tree from the intense tropical sun. Regular watering is essential to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
Pruning and shaping the tree promote healthy growth within the confines of the container. Container cultivation enables crimson king maple enthusiasts to enjoy the charm of these trees while maintaining control over their environment and accommodating limited spaces.
Is Growing Maple Trees in Tropical Climates Worth the Effort?
If you’ve ever admired the beauty of maple trees, it’s natural to wonder if they’re worth growing in a tropical climate. The truth is, while it takes extra effort, the reward can be deeply satisfying. Nurturing a maple tree in warm weather isn’t just about growing a plant; it’s about creating a living centerpiece that brings seasonal color, texture, and shade to your garden.
With thoughtful planning, choosing the right variety, and adapting care routines, many gardeners have successfully grown maples in tropical settings. Whether it’s in a container on a balcony or planted under filtered light, the result can be both visually striking and personally fulfilling.
If you’re up for the challenge, growing maple trees in the tropics isn’t just possible, it can become one of your most rewarding garden achievements. It adds a unique touch of temperate charm to your tropical space.
FAQs
Can maple trees change color in tropical regions as they do in temperate zones?
The distinct color change associated with fall might be challenging to replicate in the absence of temperate seasons. However, certain species might still exhibit color variations under specific conditions.
Are there specific growing maple trees species better suited for tropical regions?
Yes, varieties like the Japanese maple and paperbark maple (Acer griseum) have shown better tolerance to warmer conditions, making them potential candidates for tropical cultivation.
What strategies can combat the absence of cold winters in the tropics?
Employ cooling methods such as shade cloths, misting, and placing the tree in shaded locations. This helps to mitigate the effects of high temperatures and compensate for the lack of cold-induced dormancy.
Before I say goodbye, I can suggest another article I covered recently beginner-friendly tips for balcony gardening.
borshon96
Recommended

9 Effective Tips for Balcony Gardens for Beginners

Best Homemade Fertilizer: Banana Peel for Plants


Philodendron Neon Heartleaf: Your Most Obedient Houseplant