The Best Fertilizers for Vegetables: A Complete Guide for Healthy Harvests
Growing a vegetable garden requires more than just sunlight and water. To achieve proper growth, fresh produce, and high yields, your plants need proper nutrition. Fertilizers supply essential nutrients that improve soil-health, increase plant growth, and prevent-deficiencies. But with so many options available, choosing the right fertilizer can feel overwhelming.
Our blog will walk you through the best fertilizers for vegetables, explaining organic vs. synthetic fertilizers, essential nutrients, and application methods to maximize your harvest.
Know Vegetable Plant Nutrients
Plant-nutrition is key to a prosperous vegetable garden. Essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) support leafy growth, root strength, and fruit production.
Secondary nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur enhance resilience and flavor. A balanced diet ensures healthier, more productive plants.
Primary Nutrients (NPK: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium)
Vegetables require three primary nutrients, often referred to as NPK, to grow strong and healthy:
- Nitrogen (N) – Encourages leafy growth and is essential for lettuce, spinach, kale, and other greens.
- Phosphorus (P) – Supports root development and flowering, making it big for root crops like carrots, beets, and potatoes.
- Potassium (K) – Raises overall plant-health and fruit production, benefiting tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers.
Secondary Nutrients & Micronutrients
Beyond NPK, plants also need:
- Calcium (Ca) – Prevents issues like blossom-end rot in tomatoes.
- Magnesium (Mg) – Aids in chlorophyll production, essential for photosynthesis.
- Sulfur (S) – Helps produce strong, flavorful vegetables.
Maintaining a balanced nutrient supply ensures vigorous growth, disease resistance, and bountiful harvests.
Types of Fertilizers for Vegetables
Choosing the best fertilizer for a vegetable garden is big for high-yield vegetable plants. Organic options improve soil-health over time, while synthetic fertilizers offer quick nutrient increases. Understanding their benefits helps you nourish your garden effectively for strong growth and bountiful harvests.
A. Organic Fertilizers (Eco-Friendly & Sustainable)
Organic fertilizers enrich soil naturally, improving microbial activity and long-term fertility. Popular options include:
- Compost – Enhances soil structure and provides slow-release nutrients.
- Man’ure (Cow, Chicken, Horse) – High in nitrogen; great for leafy greens.
- Fish Emulsion & Seaweed Fertilizer – Liquid fertilizers rich in nitrogen and micronutrients.
- Bo’ne-Meal & Blo’od-Meal – Ideal for phosphorus-deficient soil.
- Worm Castings & Biochar – Improve soil aeration and water retention.
B. Synthetic Fertilizers for Vegetables (Fast-Acting & Precise)
If you need immediate nutrient raise, the synthetic fertilizers can be effective:
- Granular Fertilizers – Easy to apply and provide slow-release feeding.
- Liquid Fertilizers – Quickly absorbed by plants through leaves or roots.
- Slow-Release Fertilizers – Feed plants over an extended period, reducing frequent applications.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Different Vegetables
Different crops require different nutrient balances. Here’s a guide:
| Vegetable Type | Best Fertilizer Type | Recommended NPK Ratio |
| Leafy Greens (Lettuce, Spinach, Kale) | Nitrogen-rich fertilizers | 10-5-5 |
| Root Vegetables (Carrots, Beets, Potatoes) | Phosphorus-heavy fertilizers | 5-10-10 |
| Fruiting Vegetables (Tomatoes, Peppers, Cucumbers) | Balanced or potassium-rich fertilizers | 10-10-10 or 5-10-10 |
| Legumes (Beans, Peas) | Low nitrogen, high phosphorus | 5-10-10 |
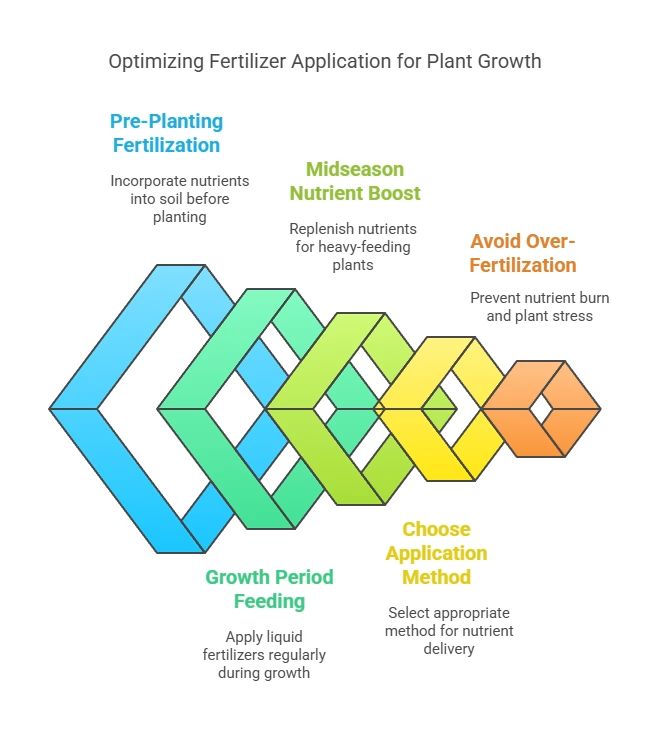
How to Apply Fertilizers for Vegetables for Maximum Growth
Applying fertilizer correctly ensures vegetables get the nutrients they need for strong growth and high yields. Timing, method, and moderation are key. Here’s how to fertilize effectively without overdoing it, so your plants stay healthy and productive all season long.
1. When to Fertilize
- Before planting – Work compost or granular fertilizer into the soil.
- During growth – Use liquid fertilizers every 2-4 weeks.
- Midseason Raise – Replenish nutrients for heavy feeders like tomatoes and squash.
2. Application Methods – Fertilizers for Vegetables
- Side-Dressing – Place fertilizer around the base of plants.
- Foliar Feeding – Spray diluted liquid fertilizer on leaves.
- Top-Dressing – Add compost around plants to slowly release nutrients.
3. Avoiding Over-Fertilization
Too much fertilizer can cause burnt leaves, weak stems, or excessive foliage growth without fruit. Always follow the recommended application rates.
DIY & Homemade Fertilizers for Vegetables
Want to go natural? Here are some DIY fertilizer options:
- Banana Peel Fertilizer – Rich in potassium, ideal for fruiting plants.
- Eggshell Tea – Raises calcium levels, preventing blossom-end rot.
- Coffee Grounds – Provides nitrogen and improves soil acidity.
- Epsom Salt Solution – Supplies magnesium for strong plant growth.
What about Black Kow?
Black Kow composted manure is produced by Black Kow, The Mature Manure Company, which has facilities specializing in composting cow manure. The composting process ensures that patho,gens and weed-seeds are eliminated while retaining essential nutrients. The result is a nutrient-rich, organic soil amendment that increases plant growth and soil structure. However, there are some Black Kow disadvantages too.
Black Kow disadvantages Compared to Other Fertilizers
| Factor | Black Kow | Synthetic Fertilizers | Compost & Organic Fertilizers |
| Nutrient Content | Low NPK (0.5-0.5-0.5) | High NPK (varies) | Moderate NPK, varies by source |
| Nutrient Release | Slow release | Fast release | Slow to moderate release |
| Odor | Mild manure smell | No odor | Varies, can be strong |
| Cost | Affordable | Can be expensive | Often free (home composting) |
| Weed Seeds | Properly composted, minimal risk | No weed seeds | Can contain weed seeds if not fully composted |
| pH Level | Neutral to slightly alkaline | Can alter soil pH | Varies depending on compost type |
| Sustainability | Eco-friendly | Often made from chemicals | Organic, but varies |
Common Fertilization Mistakes to Avoid
Fertilizing your vegetables is essential, but mistakes can harm plant-health and reduce yields. Overuse, incorrect timing, and imbalanced nutrients can all impact growth. Avoid these common fertilization errors to ensure your garden shines with productive plants.
- Over-fertilizing – Leads to weak plants prone to disease.
- Using the wrong NPK ratio – Can cause nutrient imbalances.
- Ignoring soil pH – Affects nutrient absorption. Test your soil before applying fertilizer.
- Applying fertilizer at the wrong time – Can result in nutrient loss because of rain or improper plant uptake.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the best organic fertilizer for vegetables?
Compost, man’ure, fish emulsion, and seaweed extracts are excellent organic choices.
2. How often should I fertilize vegetable plants?
Most vegetables benefit from fertilization every 2-4 weeks, but heavy feeders may require more frequent feeding.
3. Can I use lawn fertilizer for vegetables?
No, lawn fertilizers often contain herbicides or excess nitrogen that can harm vegetables.
4. What is the best fertilizer for tomatoes and peppers?
A balanced 5-10-10 or 10-10-10 fertilizer with added calcium prevents blossom-end rot and improves fruit quality.
5. What is the best fertilizer for container-grown vegetables?
Liquid fertilizers or slow-release granular fertilizers provide consistent feeding for container plants.
Conclusion
Fertilizing your vegetable garden correctly can make a huge difference in plant-health, yield, and soil sustainability. Choosing the right fertilizer, whether organic or synthetic ensures your vegetables receive the necessary nutrients for growth and delicious produce.
If you understand your plants’ nutrient needs, use organic matter, and apply fertilizers properly, you can cultivate a nice vegetable garden. Also, it will produce abundant harvests. 🌱🍅🥕
borshon96
Recommended

9 Effective Tips for Balcony Gardens for Beginners

Best Homemade Fertilizer: Banana Peel for Plants


Philodendron Neon Heartleaf: Your Most Obedient Houseplant